Idaho
The following profile is a representation of the Idaho public education state longitudinal data system (SLDS) as presented through publicly available resources of public primary, secondary and higher education, information made available to the public through the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), the Data Quality Campaign, published research articles, other third party internet resources (as noted), and direct contact with state and federal public education officials. It is not a formal program evaluation.
The information provided is intended for use by academic researchers, state and federal public education policy makers, educators, and student households.
| Introduction | Evaluation Criteria | Governance and Maintenance | Data Providers |
| Funding | Researcher Access | Public User Portal | Legal Statues |
| DQC | Contact | Schematic | State Response |
| . | |||
| Download State Profile | ISLDS Dashboard | ISLDS Website | NCES Funding: 2009 2012 |
Introduction
The Idaho State Longitudinal Data System (ISLDS)[1] is Idaho’s public education state longitudinal data system (SLDS)[2] governed by the Idaho State Board of Education (ISBE)[3]. The ISLDS, created for the purpose of collecting and analyzing Idaho’s public education data at the individual, course, institution, and system levels, aggregates data records from the breadth of the Idaho public education systems. The combined data collection systems are part of a nation-wide effort to record granular public education detail over time in order to document the entirety of students’ education experience. This information is intended to be available for analysis and public policy consideration for the purpose of producing improvements in student learning at elementary, secondary, post-secondary, and higher education levels, and to optimize labor market outcomes, individually and generally.
Idaho is one of the 47 states having received public funding to create a state longitudinal data system (SLDS). Despite state-to-state differences, each SLDS shares a common purpose of supporting research and analysis with the intent of informing individual, household, and public policy decision based on standardized criteria.
[1] The Idaho State Longitudinal Data System enables state agencies to link education and workforce data to answer questions critical to understanding Idaho’s future education workforce needs
[2] State longitudinal data systems are intended to enhance the ability of states to efficiently and accurately manage, analyze, and use education data nces.ed.gov/programs/slds/about_SLDS.asp
[3] The Idaho State Board of Education is a policy-making body for all public education in Idaho and provides general oversight and governance for public K-20 education boardofed.idaho.gov/
Return to top of page
Evaluation Criteria
This review assesses the overall quality of the ISLDS as an SLDS by considering the nature of the organization maintaining the data system, those agencies and institutions providing inputs to the data system, and to which agencies and institutions the data systems’ outputs are available. The assessment also considers the data system’s funding mechanisms, internal and external researcher data accessibility, the quality of the data system’s public user interface (dashboard), and the data system’s current Data Quality Campaign (DQC)[1] ranking.
[1] The Data Quality Campaign is a national, nonprofit organization leading the effort to bring every part of the education community together to empower educators, parents, and policymakers with quality information to make decisions that ensure students excel dataqualitycampaign.org/
Return to top of page
Governance and Maintenance
The ISLDS is governed by ISBE, the state agency which is constitutionally and statutorily charged with supervising public education in Idaho. The ISBE created the ISLDS to measure how Idaho’s public education system is preparing students to perform at higher education institutions and/or in the state’s workforce. The IBSE created the Idaho Data Management Council (IDMC) to oversee and improve the ISLDS throughout its development and operations. The IDMC is comprised of representatives from the state agencies and institutions that provide data to the ISLDS. These state agencies and institutions are the Idaho State Board of Education (ISBE), the Idaho State Department of Education (ISDE)[1], Idaho’s post-secondary institutions, Idaho’s public schools and the Idaho State Department of Labor (ISDL)[2]. The council provides direction and makes recommendations to the ISBE on policies and procedures for the development and usage of the system. It also provides progress reports to the ISBE, detailing status updates on current system development projects and reporting any issues concerning the ISLDS that require the ISBE’s consideration.[3]
The state agencies and institutions represented on the IDMC are all involved with ISLDS in some matter or form. Each agency and institution either provide data records to the ISLDS through their in-house data systems or supervise the students or workers whose information is contained within the ISLDS. These agencies and institutions have established agreements between themselves to allow the ISLDS to link their data records into aggregated data files on which longitudinal reporting and analysis can be performed. Each agency and institution seeks to use these reports and analysis to identify how their specific operations are impacting the education and/or workforce outcomes of Idaho youth.
The IDMC is responsible for ensuring that the data records contained within the ISLDS are accurate and verified. The council conducts annual reviews of these data records to confirm that data records collected within the ISLDS meet the data quality requirements set by the ISBE. The council also is mandated with ensuring the safety and privacy of the data records contained within the ISLDS. The ISLDS data is housed on a secure server hosted between the ISBE and the ISDE. The council has established a set of procedures that must be followed to access and utilize the data contained in the data warehouse. Only approved employees within the ISBE and ISDE can access this data, these employees must have received specific security training from training plans established by ISBE, ISDE and ISDL. The council has set these requirements to certify that the state has taken adequate steps to protect the student level education information contained within the ISLDS data warehouse.[4]
[1] The Idaho State Department of Education is a government agency supporting schools and students. It is responsible for implementing policies, distributing funds, administering statewide assessments, licensing educators, and providing accountability data sde.idaho.gov/
[2] The Idaho State Department of Labor seeks to connect business, education and workforce, link job seekers with employers and help people with career and life transactions
[3] Information obtained from Idaho Data Management Council’s Policies and Procedures boardofed.idaho.gov/research_stats/documents/data_management_council/DMC%20Policies%20approved%2009-03-15.pdf?cache=1479316740807
[4] See ref. 7
Return to top of page
Data Providers
The ISLDS receives data records from the ISDE’s K-12 data system, the data systems of the post-secondary education institutions represented on the IDMC, and the ISDL’s wage record system. These data records are compiled into the ISLDS data warehouse, a secure server jointly hosted by the ISBE and the ISDE. This data repository has the systemic capabilities to perform unit-level record linkages between these data records. The ISLDS can generate longitudinal reports analyzing these data records on an ad-hoc basis.
The ISLDS receives K-12 data records from the ISDE’s Education Analytics System of Idaho (EASI), a statewide K-12 student information system. EASI collects individual level student information on all students in the Idaho K-12 public education system. This information includes attendance and enrollment information, student performance on the Idaho Standards Achievement Test, graduate and drop-out information, student course information and other education relevant information. This system links individual student data records across time as they progress through the state’s K-12 public education system. This individual student level information is used to analyze student outcomes through their education process and yields invaluable information to policy makers and other interested parties about the effects of education programs and initiatives on student achievement. The EASI provides this individual student level information by assigning a unique student identifier variable to each student that enters into the Idaho K-12 public education system. This unique student identifier is assigned by the ISDI’s unique student ID system (EDUID), a system that has the capability to assign ID’s to all student in the K-12 public education system. This unique ID will remain with the student throughout their K-12 education experience, as well as their higher education experience if they attend a post-secondary education institution. [1]
The ISLDS receives post-secondary data records from the following post-secondary education institutions: Boise State University, Idaho State University, College of Southern Idaho and North Idaho College. Each of these institutions have their own student data collection systems. In 2010, these institutions processed their enrollment files through ISDE’s EDUID system to obtain the unique ID’s of students who had already been assigned unique ID’s through the Idaho K-12 public education system. The EDIUD system then generated new ID’s for any students that did not attend the Idaho K-12 public education system or were not previously accounted for. This process enables the K-12 data records provided by ISDE and these post-secondary data records to be matched and linked for longitudinal analysis purposes. [2]
The ISLDS also receives workforce data records from the ISDL’s wage record system. The data records provided by the ISDL contain individual level information on workers’ employment status, wages, employer, demographic characteristics and industry. These data records also contain a labor unique ID (LABUID) that is assigned to each individual in the wage record system and matched to an individual’s Social Security Number. The LABUID acts as a proxy to an individual’s Social Security Number and is the necessary linkage component between education and workforce data within the ISLDS. The ISDL created the LABUID so that the ISLDS data warehouse would not need to store Social Security Numbers.[3]
[1] Information obtained from Idaho 2012 SLDS Grant application nces.ed.gov/programs/slds/pdf/Idaho2012.pdf
[2] See ref. 9
[3] See ref.9
Return to top of page
Funding
The ISBE applied for federal funding through the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), an agency of the United States Department of Education, in 2009 and 2012 and was awarded two grants, the 2009 SLDS Grant and the 2012 SLDS Grant, for the purpose of developing the ISLDS. The 2009 SLDS Grant awarded $5,916,520 to the ISBE for the purpose of establishing the foundational infrastructure of the ISLDS. This funding was used to pay for the various costs associated with developing a data system, including personnel costs, travel costs, equipment costs, contractual costs, and indirect costs. The proposed outcomes of the funding were to:[1]
- Contract with ESP Solutions for an enterprise architecture assessment and design
- Hire a CIO with experience implementing and managing enterprise systems
- Create a project management office
- Create a data dictionary and identify data ownership
- Implement a unique student ID system statewide
- Define requirements to re-engineer core data collection systems
- Plan for a statewide portal with a single-sign-on security for all systems
The 2012 SLDS Grant awarded ISBE $3,101,632 for the purpose of further developing and enhancing the ISLDS. This funding was used to pay for the various costs associated with developing a data system, including personnel costs, travel costs, equipment costs, contractual costs, and indirect costs. The proposed outcomes of the funding were to:[2]
- Develop the workforce database
- Create a workforce longitudinal database
- Expand ISLDS to include aggregate workforce data elements
- Create an Idaho Institutional Review Board
- Sign MOU’s and create Labor Unique ID system
- Pursue a data exchange with the Department of Transportation to populate SSN
- Produce extensive workforce summary reporting
- Improve visibility into workforce outcomes
- Enhance the EDUID system
- Investigate EDUID improved matching opportunities
- EDUID system changes
- Improve match rates
- Research Data Request Website
- Receive input from stakeholders
- Design request process
- Develop website and implement workflow
- Streamline research request process
[1] Information obtained from Idaho 2009 SLDS Grant application nces.ed.gov/programs/slds/pdf/Idaho2009.pdf
[2] See ref. 9
Return to top of page
Research Accommodation
Interested parties who wish to use data records contained within the ISLDS data warehouse for research purposes must submit a data request to the IDMC that adheres to their data request process. The data request must provide the following information and meet the following requirements:[1]
- Submitted request – The abstract of what the researcher project’s objectives are and what data is need, including the timeframe and types of data. This information is utilized to determine who the internal ISLDS sponsor should be, whether the ISLDS is the correct data source, and if the request can be satisfied by an existing solution. Any requests that pertain to a single institution or K-12 data will be reviewed with the institution or ISDE and either transferred to them or fulfilled by the ISLDS at their request.
- Sponsor assignment – Every research request will be assigned a sponsor. The sponsor is responsible for guiding the request through the workflow process.
- Sponsor approval – A sponsor must initially approve the request.
- MOU completed – Each research request that requires de-identified student level data will be required to have a separate Memorandum of Understanding completed and approved.
- SQL submission – If the researcher is capable of generating the SQL statement necessary to extract the data, they will submit the SQL statement. If they need assistance, internal resources will be designated to complete this step.
- SQL approval – The ISLDS contains data that is owned by the ISBE, ISDE, ISDL, etc. The SQL will be reviewed against the MOU’s and a recommendation will be prepared for the IDMC.
- IDMC approval – This is the final approval point before data extraction and will alert the ISLDS staff to create the data set and contact the researcher.
- Data Set Transferred – the ISLDS has a secure file transfer system that will be utilized to transfer the dataset to the researcher. This dataset will be labeled with the date that reflects the amount of time granted to fulfill the request.
- Research submission for approval – The researcher will transfer their final draft report for review to ensure no disclosure of Personally Identifiable Information
- Research approved – Once the internal review is complete and any needed changes are made by the researcher, the researcher will be given approval to release the results.
[1] See ref. 9
Return to top of page
Public User Portal
The ISLDS does not have a public user portal at this time.
Return to top of page
Legal Statutes
There is currently no legal statutes passed by the Idaho legislature directly addressing the ISLDS, however, the Idaho legislature Senate passed Senate Bill No. 1296 in 2014 which contains the following information:[1]
“RELATING TO EDUCATION; TO PROVIDE A SHORT TITLE; TO PROVIDE LEGISLATIVE 3 INTENT; AMENDING CHAPTER 1, TITLE 33, IDAHO CODE, BY THE ADDITION OF 4 A NEW SECTION 33-133, IDAHO CODE, TO PROVIDE DEFINITIONS, TO PROVIDE 5 FOR A RESPONSIBLE ENTITY, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO A DATA 6 INVENTORY AND DICTIONARY OR INDEX, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO 7 CERTAIN POLICIES AND PROCEDURES, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO 8 THE STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION AND THE STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION EN- 9 SURING THAT CERTAIN VENDORS SHALL COMPLY WITH THE LAW, TO PROVIDE FOR A 10 CIVIL ENFORCEMENT ACTION, TO PROVIDE FOR A COURT ACTION, TO PROVIDE FOR 11 A PENALTY, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO DATA DEEMED CONFIDEN- 12 TIAL, TO PROVIDE FOR EXCEPTIONS, TO PROVIDE FOR A DATA SECURITY PLAN, TO 13 ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO COMPLIANCE WITH CERTAIN POLICIES AND 14 LAWS, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO CERTAIN CONTRACTS, TO PRO- 15 VIDE FOR NOTIFICATION TO THE GOVERNOR AND THE LEGISLATURE, TO PROVIDE 16 FOR RULES, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO EXISTING COLLECTION OF 17 STUDENT DATA, TO ESTABLISH PROVISIONS RELATING TO A PARENT OR GUARDIAN 18 REQUEST FOR THEIR CHILD’S STUDENT RECORD, TO PROVIDE FOR A MODEL POLICY 19 AND TO PROVIDE FOR PENALTIES; AND DECLARING AN EMERGENCY.” (Senate Bill No. 1296)
[1] Information obtained from Idaho Senate Bill No. 1296 legislature.idaho.gov/legislation/2014/S1296.pdf
Return to top of page
DQC
The Data Quality Campaign (DQC) is a nonprofit, nonpartisan national advocacy organization that evaluates each state’s longitudinal data system to determine how effectively each state uses their data system for education improvement purposes. The DQC’s annual survey, Data for Action (DFA)[1], measures each state’s progress towards implementing the 10 Essential Elements of Statewide Longitudinal Data Systems and the Ten State Actions to Ensure Effective Data Use[2], a set of elements and policy actions proposed to produce quality data systems and increase student achievement within in each state.
Idaho has currently met each of the 10 essential elements:
- Element 1 – Statewide student identifier
- Element 2 – Student-level enrollment data
- Element 3 – Student-level test data
- Element 4 – Information on untested students
- Element 5 – Statewide teacher identifier with a teacher-student match
- Element 6 – Student-level course completion data
- Element 7 – Student-level SAT, ACT, and Advanced Placement exam data
- Element 8 – Student-level graduation and dropout data
- Element 9 – Ability to match student-level P-12 and higher education data
- Element 10 – State data audit system
Idaho has currently met 7 of the 10 state actions:
- State Action 2 – Create stable, sustainable support for longitudinal data systems
- State Action 3 – Develop governance structures for longitudinal data systems
- State Action 4 – Build state data repositories
- State Action 5 – Provide timely, role-based access to data
- State Action 6 – Create progress reports with student-level data for educators, students, and parents
- State Action 7 – Create reports with longitudinal statistics to guide system-level change
- State Action 9 – Implement policies and promote practices to build educators’ capacity to use data
Idaho has failed to meet the following state actions:
- State Action 1 – Link state K-12 data systems with early learning, workforce, and other critical state agency data systems
- State Action 8 – Develop a purposeful research agenda
- State Action 10 – Promote strategies to raise awareness of available data
Data Quality Campaign score: 7/10
It should be noted that that Data Quality Campaign assessed each state’s progress towards completing the state actions in 2014.
[1] DQC’s annual survey, Data for Action (DFA), is a powerful tool to inform efforts in education to better use data in decision making. It is a series of analyses that highlight state progress and key priorities to promote the effective use of longitudinal data to improve student achievement
[2] DQC’s 10 Essential Elements of Statewide Longitudinal Data Systems and 10 State Actions to Ensure Effective Data Use provide a roadmap for state policymakers to create a culture of effective data use in which quality data are not only collected but also used to increase student achievement
Return to top of page
Contact
Idaho State Board of Education
Andy Mehl
Educational Analytics System of Idaho Program Manager
Email: andy.mehl@osbe.idaho.gov
Phone: (208) 332-1586
Return to top of page
Schematic
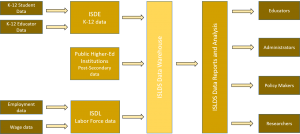
This schematic is offered to provide a simplified, visual presentation of the ISLDS and the channels through which data flows into and out of the SLDS. The entities on the far left side of the schematic represent the data record providers to the ISLDS. The entities in the middle of the schematic represent the ISLDS and public user portal. The entities on the far right side of the schematic represent the parties intended to receive benefits from the outputs generated by the ISLDS.
Return to top of page
State Response
SLDS stakeholders listed under Contacts (above) have been provided a copy of this State Profile and given an opportunity to provide comments in response. No comments have been received for this state to date.